-
Research
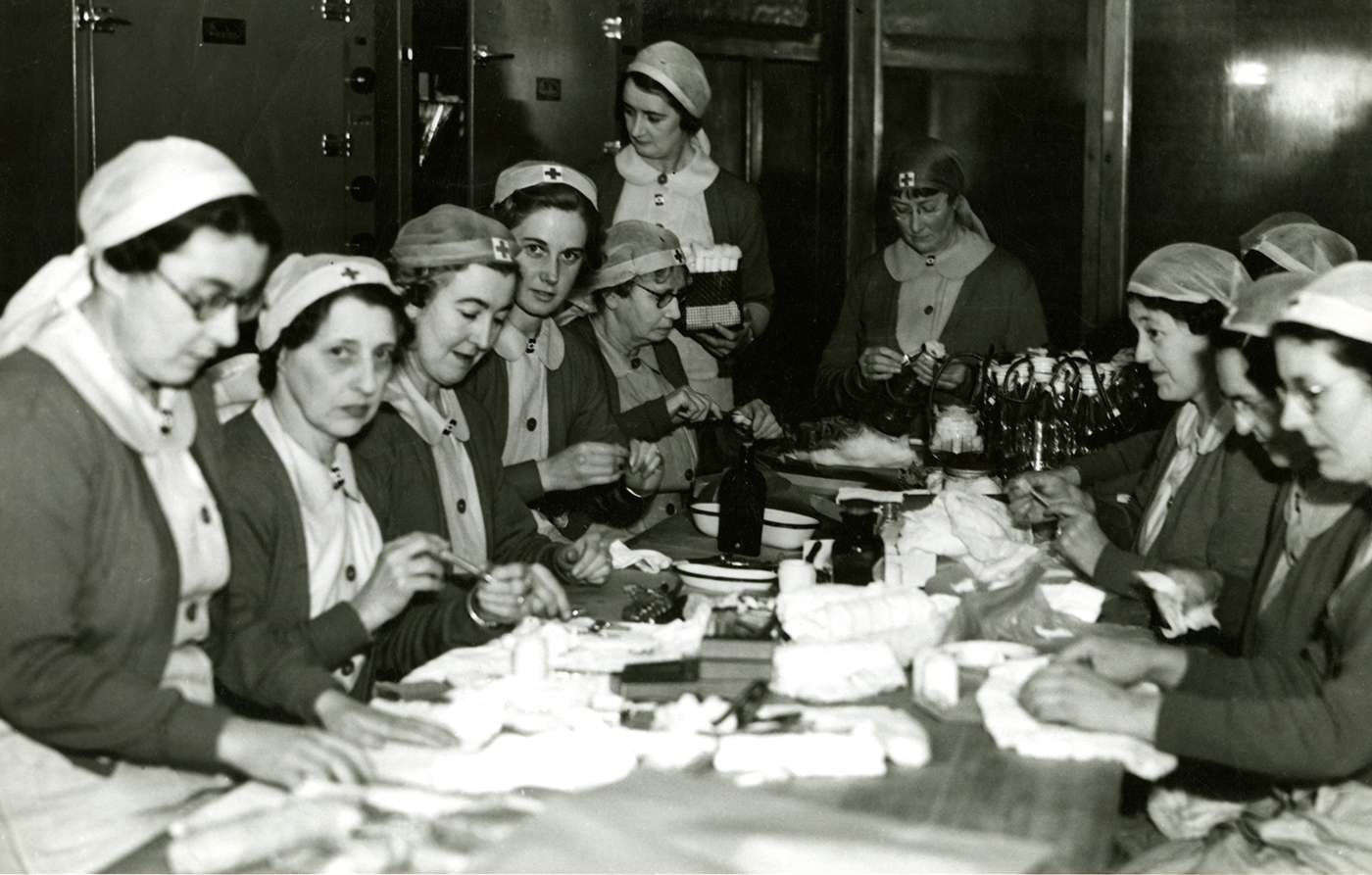
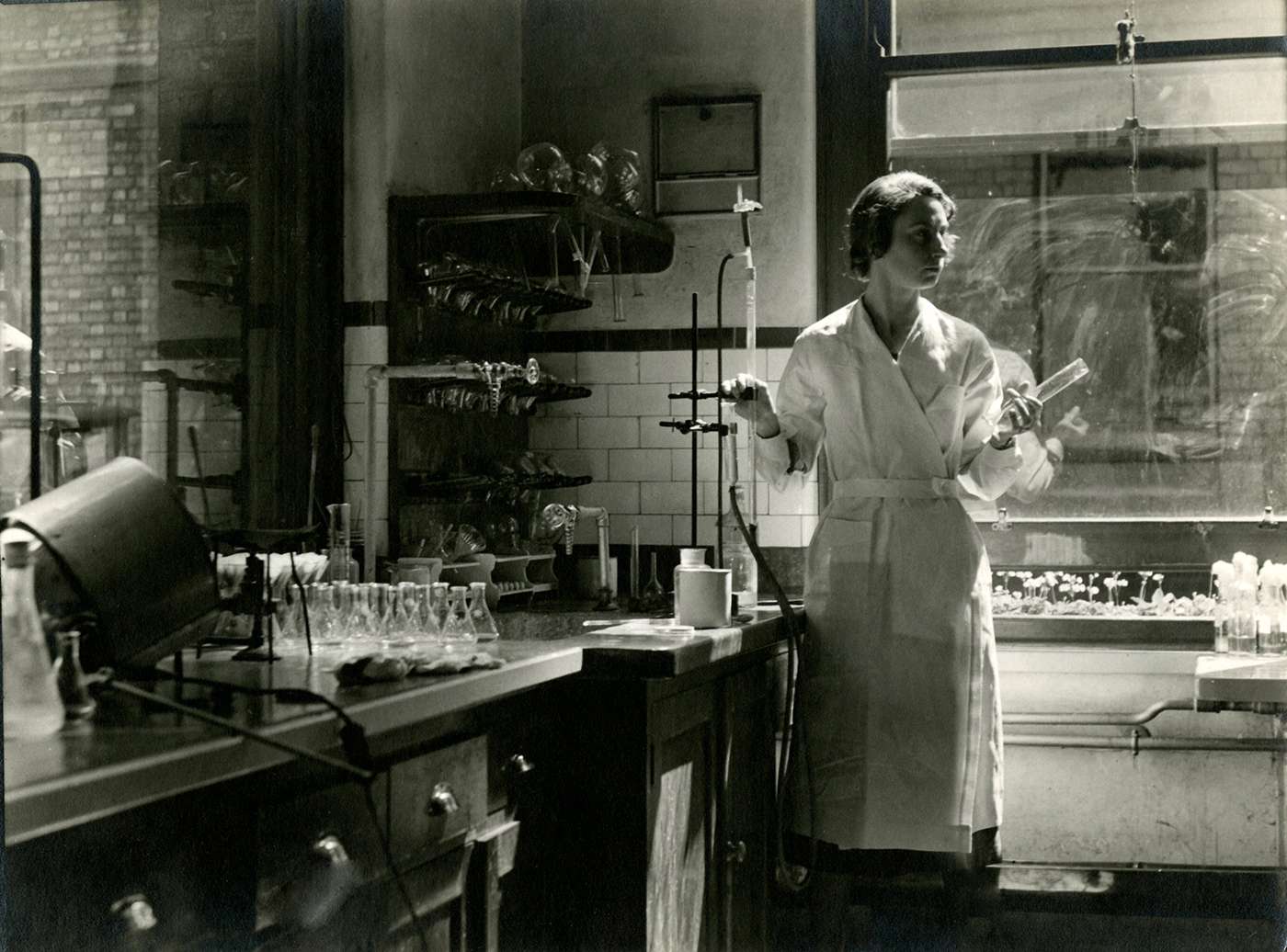
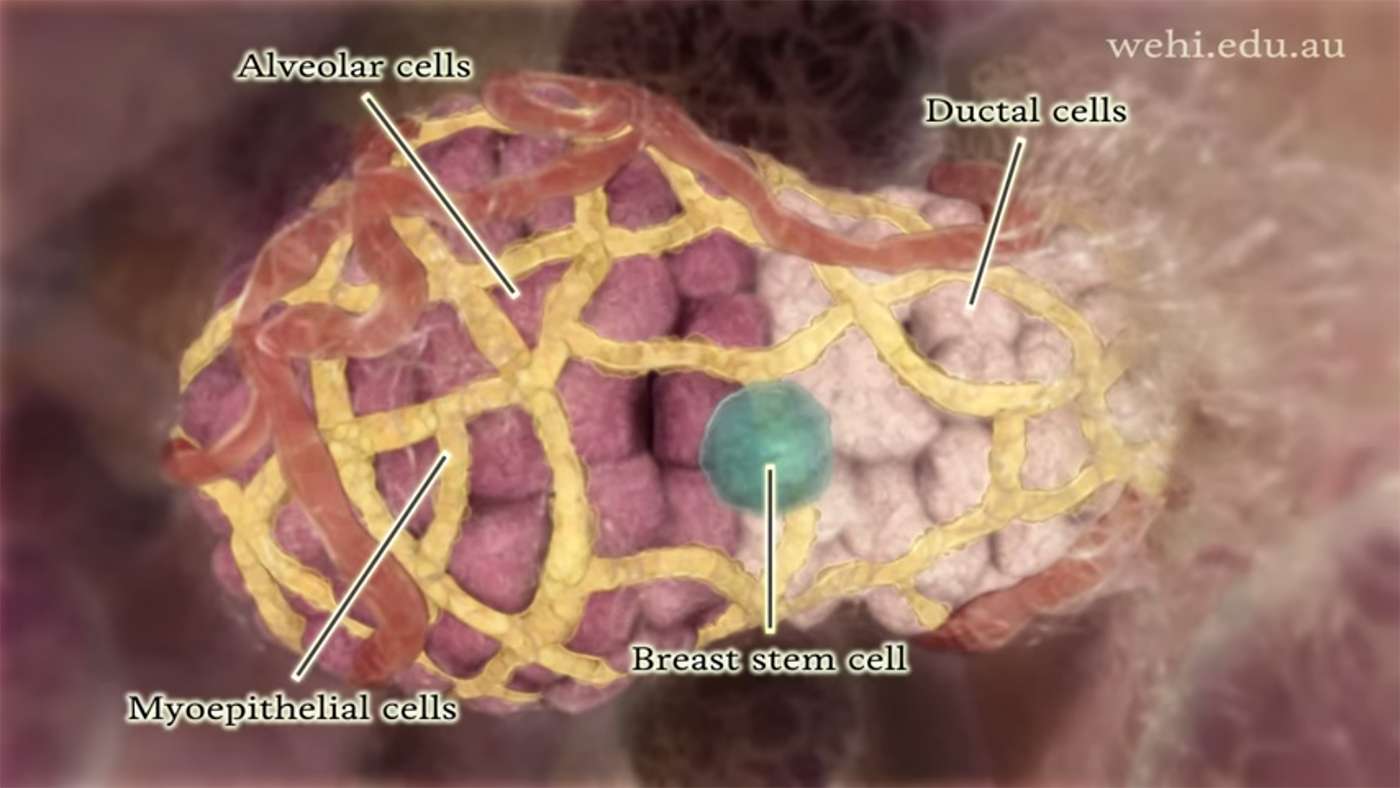
Our researchFinding better ways of detecting and treating a wide range of diseases, and helping our community to live long and healthy lives.
-
About
About WEHIWhere the world’s brightest minds collaborate and innovate to make discoveries that will help us to live healthier for longer.
-
Careers and education
Working and studying at WEHIWEHI promotes a scientific environment that emphasises innovation, collaboration and excellence.