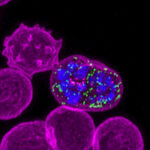
Malaria is a disease that is caused by a parasite. The parasite can get into our bodies when we are bitten by certain types of mosquitoes that are infected with the parasite. These mosquitoes are most common in hot, tropical regions like Africa and Asia.
While malaria is preventable and curable, it still claims the lives of more than 600,000 people worldwide every year. The disease is most deadly to pregnant women and children aged under five, particularly in poorer countries where malaria-fighting medicine is not always accessible.
Malaria is a major cause of death and loss of productivity in many countries in South-East Asia, the Pacific and Africa.