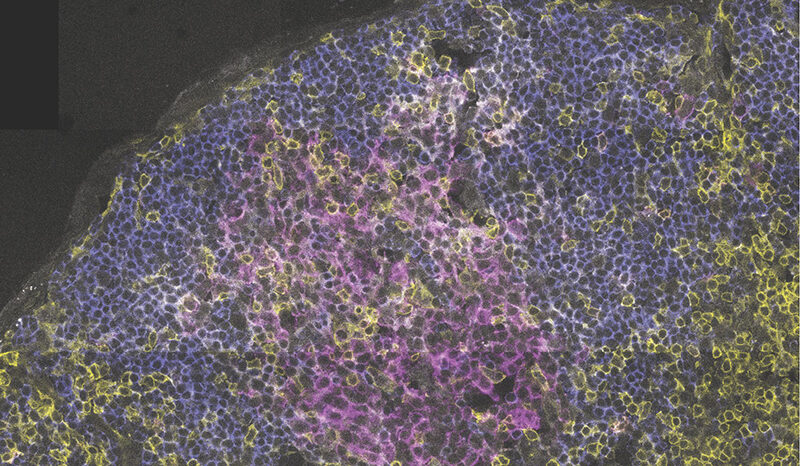
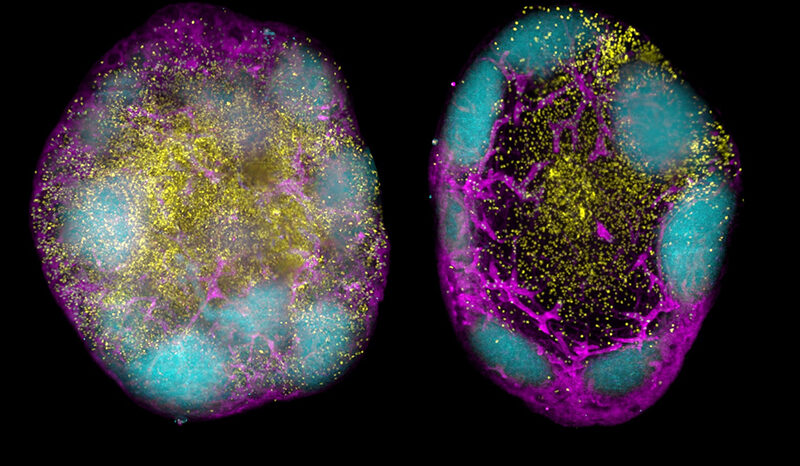
Ashayeripanah M, Coughlan H, Zhang S, Yan J, Bandala-Sanchez E, Jenika D, Lin D, Tullett KM, Naik SH, Groom JR, Lahoud MH, Belz GT, Huntington ND, Smyth GK, Nutt SL, Chopin M. Interleukin 4 selectively expands functional type 1 conventional dendritic cells from bone marrow progenitors. Cell Reports. 2026;45(1):10.1016/j.celrep.2025.116772
Keating N, Doggett K, Bidgood GM, Meza Guzman LG, Dagley LF, Li K, Williams BE, Gabrielyan A, Alvarado C, Broomfield BJ, Duckworth BC, Hockings C, Yousef J, Leong E, Morris R, Kueh A, Garnham AL, Giner G, Casanova J-L, Boisson-Dupuis S, Babon JJ, Linossi EM, Tate MD, Groom JR, Nicholson SE. ARAP2 regulates responses to interferon-gamma by restricting SOCS1. Cell Reports. 2025;44(12):10.1016/j.celrep.2025.116667
Dalit L, Tan CW, Sheikh AA, Munnings R, Howson LJ, Alvarado C, Hussain T, Zaini A, Cooper L, Kirn A, Hailes L, Nguyen A, Williams BE, Zheng MZM, van de Sandt CE, Mackay LK, Flanagan KL, Kedzierska K, Harris N, Juno JA, Zaph C, La Gruta NL, Davis MJ, Nutt SL, Good-Jacobson KL, Bryant VL, Groom JR. Divergent cytokine and transcriptional signatures control functional T follicular helper cell heterogeneity. Nature Immunology. 2025;26(10):10.1038/s41590-025-02258-9
Broomfield BJ, Tan CW, Qin RZ, Abberger H, Duckworth BC, Alvarado C, Dalit L, Lee CL, Mugan RS, Mazrad ZAI, Muramatsu H, Mackiewicz L, Williams BE, Chen J, Takanashi A, Fabb S, Pellegrini M, Rogers KL, Moon WJ, Pouton CW, Davis MJ, Nutt SL, Pardi N, Wimmer VC, Groom JR. Transient inhibition of type I interferon enhances CD8+ T cell stemness and vaccine protection. Journal of Experimental Medicine. 2025;222(5):10.1084/jem.20241148
Broomfield BJ, Groom JR. Defining the niche for stem-like CD8+ T cell formation and function. Current Opinion in Immunology. 2024;89:10.1016/j.coi.2024.102454
Cooper L, Xu H, Polmear J, Kealy L, Szeto C, Pang ES, Gupta M, Kirn A, Taylor JJ, Jackson KJL, Broomfield BJ, Nguyen A, Gago da Graça C, La Gruta N, Utzschneider DT, Groom JR, Martelotto L, Parish IA, O’Keeffe M, Scharer CD, Gras S, Good-Jacobson KL. Type I interferons induce an epigenetically distinct memory B cell subset in chronic viral infection. Immunity. 2024;57(5):10.1016/j.immuni.2024.03.016
Abberger H, Groom JR. Macro-clusters: CD301b+ DCs prime Th2 responses. Journal of Experimental Medicine. 2024;221(4):10.1084/jem.20240088
Torres SV, Man K, Elmzzahi T, Malko D, Chisanga D, Liao Y, Prout M, Abbott CA, Tang A, Wu J, Becker M, Mason T, Haynes V, Tsui C, Shakiba MH, Hamada D, Britt K, Groom JR, McColl SR, Shi W, Watt MJ, Le Gros G, Pal B, Beyer M, Vasanthakumar A, Kallies A. Two regulatory T cell populations in the visceral adipose tissue shape systemic metabolism. Nature Immunology. 2024;25(3):10.1038/s41590-024-01753-9
Tellier J, Tarasova I, Nie J, Smillie CS, Fedele PL, Cao WHJ, Groom JR, Belz GT, Bhattacharya D, Smyth GK, Nutt SL. Unraveling the diversity and functions of tissue-resident plasma cells. Nature Immunology. 2024;25(2):10.1038/s41590-023-01712-w
Zaini A, Dalit L, Sheikh AA, Zhang Y, Thiele D, Runting J, Rodrigues G, Ng J, Bramhall M, Scheer S, Hailes L, Groom JR, Good-Jacobson KL, Zaph C. Heterogeneous Tfh cell populations that develop during enteric helminth infection predict the quality of type 2 protective response. Mucosal Immunology. 2023;16(5):10.1016/j.mucimm.2023.06.007