Cryptococcosis is a disease caused by infection with the fungus Cryptococcus. It is potentially fatal, particularly in people with a weakened immune system.
The Cryptococcus fungus is present in the environment, particularly in areas contaminated with bird droppings. It can infect skin and wounds. The most common way Cryptococcus infects humans is by being inhaled.
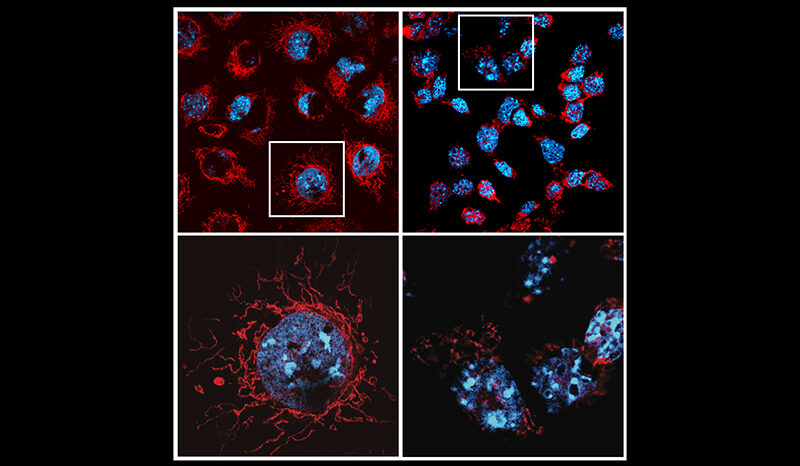
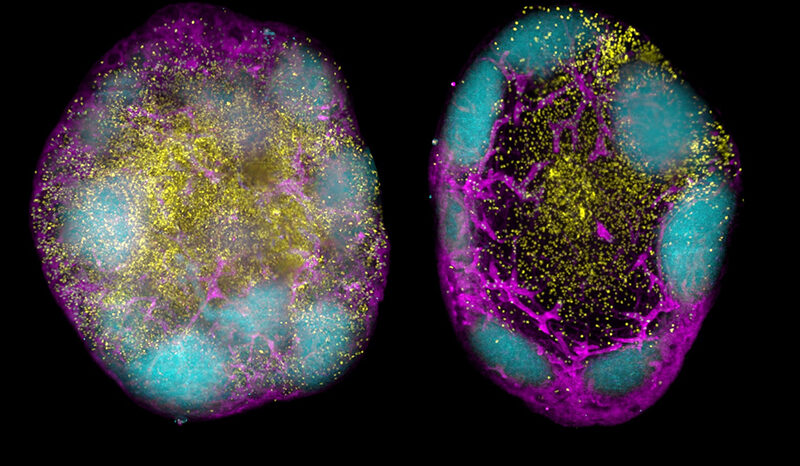
When Cryptococcus is inhaled, it can grow within the lungs. In some people this causes a slowly developing lung disease. Within the lungs, immune cells called macrophages can also be infected. The Cryptococcus cells can survive and divide within macrophages.
Cryptococcus lung infections can lie dormant for months to years. The infection can also spread to other parts of the body. This is more likely to occur in people with a weakened immune system.
In the brain, Cryptococcus infection causes cryptococcal meningitis. This is a serious inflammatory disease that can cause:
- Confusion and hallucinations
- Brain damage
- Hearing loss
- Hydrocephalus (accumulation of fluid on the brain)
- Coma
Untreated cryptococcal meningitis is fatal in an estimated 30 to 70 per cent of people.
More than 180,000 people die from cryptococcosis every year, mostly in sub-Saharan Africa. It is the leading cause of death in people with HIV and AIDS in this region.