A silent threat to gut health
About one in three Australians currently live with chronic inflammatory disease, like coeliac disease, inflammatory bowel disease and rheumatoid arthritis.
But how this inflammation arises and causes disease remains largely unknown.
Dr Cyril Seillet, a senior author on the paper, said the team’s findings were a significant breakthrough that could help pinpoint how chronic inflammation occurs at the source.
“We’ve shown that every meal we consume actively shapes our gut health,” Dr Seillet said.
“The more saturated fats we eat, the more inflammation that builds up – gradually weakening our gut defences and increasing our susceptibility to chronic inflammation.
“But this inflammation build-up is initially silent, remaining hidden in our bodies until years later, where it can present as chronic inflammation.”
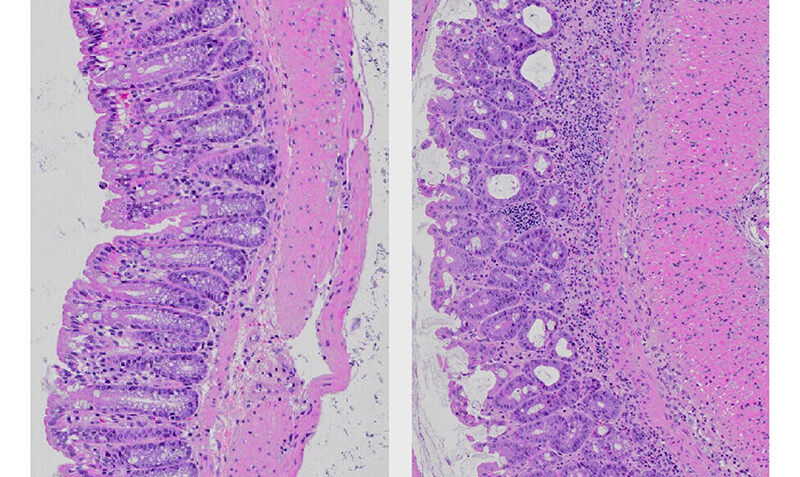
Researchers were able to detect microscopic changes to the gut health and function in mice even after a few high-fat meals, despite the mice lacking any visible symptoms of inflammation, such as weight gain.
“This shows how easily inflammation can develop without immediate warning signs,” Dr Seillet said.
“While occasional high-fat meals won’t impair your gut protection barrier, a consistent diet that is high in saturated fats is laying the foundation for chronic gut inflammation to present in future.”